Contents
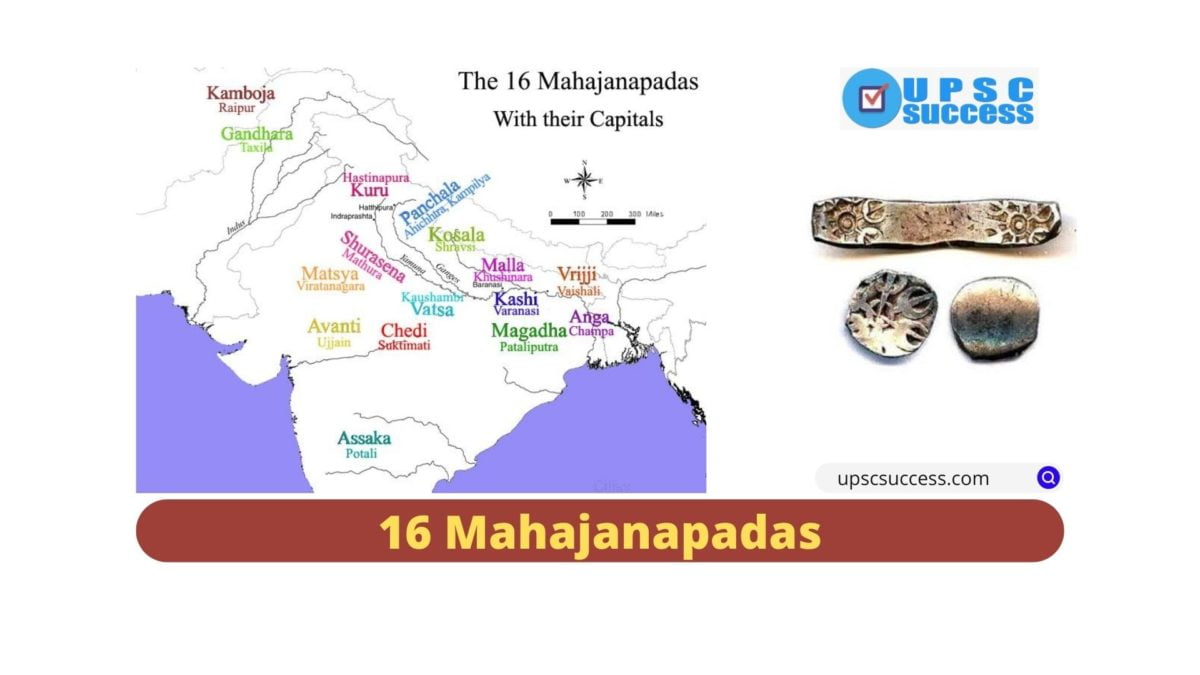
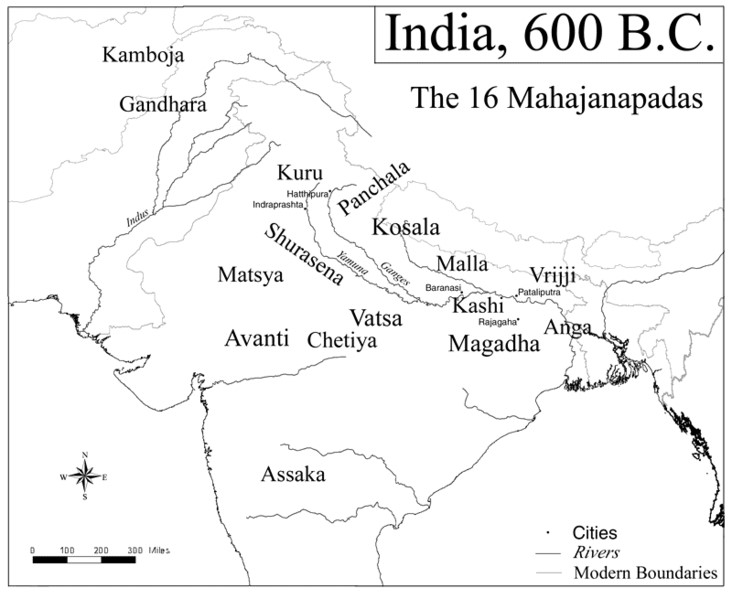
The Mahajanapadas were a set of sixteen kingdoms that existed in ancient India. It all began when the tribes (Janas) of the late Vedic period decided to form their own territorial communities, which eventually gave rise to new and permanent areas of settlements called ‘states’ or ‘janapadas.’
The period of Mahajanpadas (600 BCE) is also known as the Period of 2nd urbanization (IVC was the 1st urbanization) as the centre of polity and economy shifted from India’s North-west to Eastern states (mainly Bihar).
At that time there were 16 such Mahajanapadas (as per the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya)
1. Anga
Capital: Champa
Modern location: Munger and Bhagalpur, Bihar
- Reference found in the Mahabharata and Atharva Veda
- Bimbisara taken over Anga
2. Magadha
Capital: Rajagriha
Modern location: Gaya and Patna
- Magadha was semi-Brahmanical habitation.
- Magadha and Anga was divided by river Champa.
- Later it became a center of Jainism and Buddhist
3. Kasi
Capital: Kasi
Modern Location: Banars
It got its name from the rivers Varuna and Asi according to Matsya Purana. Dhritarashtra once ruled over Kashi and Anga
4. Vatsa
Capital: Kausambi
Modern Location: Allahabad
- Vatsa is also known as Vamsa
- Ruler Udayana made Buddhism a state religion.
5. Kosala
Capital: Sravasti
Modern Location: Eastern Uttar Pradesh ( Ayodhya)
- Ayodhya was an important town in Kosala.
- It was merged in the Magadha by the Magadha ruler, Ajatashatru.
- Kosala also included the tribal republican territory of Sakyas of Kapilvastu.
6. Saurasena
Capital: Mathura
Modern Location: Western Uttar Pradesh
- This place was a centre of Krishna worship at the time of Megasthenes.
- The most famous ruler was Avantiputra.
7. Panchala
Capital: Ahichchatra and Kampliya
Modern Location: Western Uttar Pradesh
Later the nature of governance shifted from monarchy to republic. Kanauj was an important town in this kingdom
8. Kuru
Capital: Indraprastha
Modern Location: Thaneswar, Meerut and Southeastern Haryana
The area around Kurukshetra was apparently the site for Kuru Mahajanapada. It moved to a republic form of governance.
9. Matsya
Capital: Viratnagar. Modern Location: Jaipur
It got its independence from the Chedi kingdom (ruled by King Sahaja) under the leadership of Virat Raja.
10. Chedi
Capital: Sotthivati
Modern Location: Yamuna and Narmada belt
This was cited in the Rigveda. It is located in the present-day Bundelkhand region.
11. Avanti
Capital: Ujjaini or Mahismati.
Modern Location: Malwa and Madhya Pradesh
Avanti was significant in relation to the rise of Buddhism. It was the most vulnerable of all the mahajanapadas and was ruled by many kingdoms
12. Gandhara
Capital: Taxila
Modern Location: Rawalpindi
Gandhara is cited in the Atharva Veda. It was significant for international commercial activities.
13. Kamboja
Capital: Pooncha
Modern Location: Rajori and Hajra
It is situated in present day Kashmir and Hindukush.
Several literary sources mention that Kamboja was a republic.
>>>>>>
14. Ashmaka or Assaka
Capital: Pratisthan/ Paithan
Modern Location: Bank of Godavari
Brahamdatta was its most important ruler.
15. Vajji
Capital: Vaishali
Modern Location: North Bihar
Vajji was the seat of a united republic of eight smaller kingdoms of which Lichchavis, Janatriks and Videhas were also members.
16. Malla
Capital: Kusinara
Modern Location: Deoria and Uttar Pradesh, Gorakhpur region
Religion was Buddhism. Malla was a republic
FAQs
There were sixteen of such Mahajanapadas: Kasi, Kosala, Anga, Magadha, Vajji, Malla, Chedi, Vatsa, Kuru, Panchala, Machcha, Surasena, Assaka, Avanti, Gandhara and Kamboja.
Mahajanapadas were formed sixth century BC onward. The most prominent feature of Mahajanapadas is the formation of states. With the rise of Mahajanapadas, the political history of North India became clearer. 16 Mahajanapadas had both republics and monarchies.
Most of the Mahajanapadas were established by conglomerating several Janapadas. One such example is the Kosala which incorporated the Janapada of Sakyas and of Kashi.