Contents
coastal plains in India
- The coastline of India is about 7517 Km long.
- 6100 km of mainland coastline and 1417 km of Indian islands.
- 13 States and UTs have coastal plains in India
- The coastline of the India States & UTs wise:
- Gujarat – 1215 Km
- Andhra Pradesh – 974Km
- Tamil Nadu – 907 Km
- Maharashtra – 652.6 Km
- Kerala – 569.7 Km
- Odisha – 476.4 Km
- Karnataka – 280 Km
- Goa (with Daman & Diu) – 160.5 Km
- West Bengal – 157.5 Km
- Puducherry – 30.6 Km (UT)
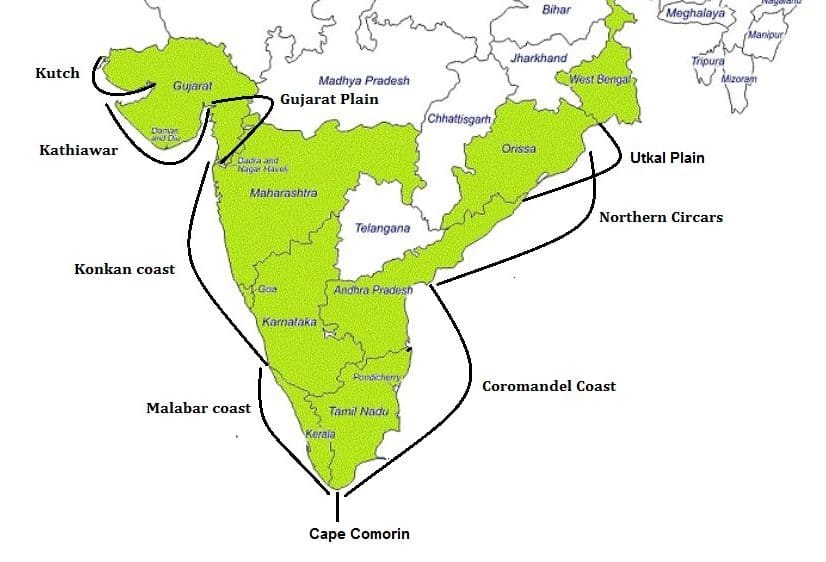
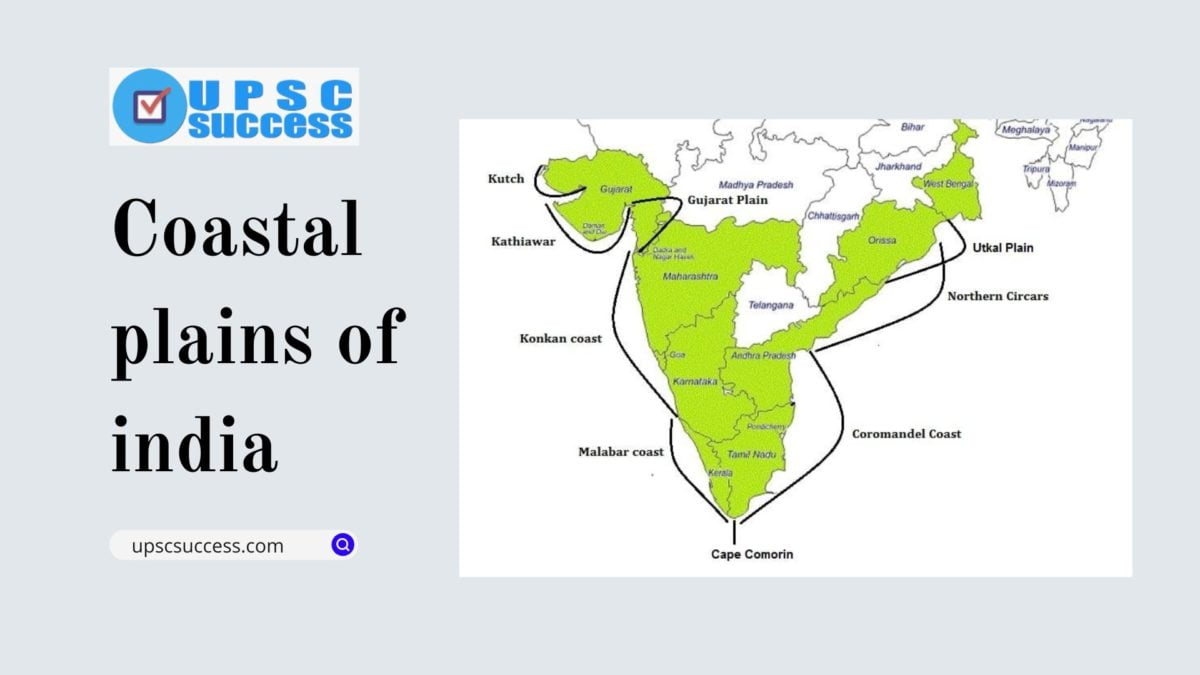
Western Coastline of India
- Kutch and Kathiawar coast
- Gujarat Plain
- Konkan coast
- Goan coast
- Malabar coast
Eastern Coastline of India
- Utkal Plain
- Andhra Plain
- Coromandel Coast
Western Coastal Plains of India
- It extends from Rann of Kutch in the north to Cape Comorin (Kanniyakumari).
- Western coastal plains in India are an example of a submerged coastal plain.
- Because of this submergence, it is a narrow belt with an average width of about 65 km
- It provides natural conditions for the development of ports and harbors.
- Kandla, Mazagaon, JLN port Navha Sheva, Marmagao, Mangalore, Cochin, etc. are some important natural ports located along the west coast.
- Western coastal plains of India are narrow in the middle and get broader towards the north and south.
- Rivers flowing through this coastal plain do not form any delta but a few estuaries.
- The estuaries of the Narmada and the Tapi are important.
Kutch & Kathiawar Coast
- Kutch Coast is an extension of the Peninsular plateau (made of the Deccan Lava).
- It is treated as part of the Western coastal plains of India as they are now levelled down.
- The Kutch Peninsula was an island surrounded by seas and Kutch lagoons.
- These seas and lagoons were later filled by sediment brought by the Indus River which used to flow through this area.
- Lack of rains in recent times has turned it into an arid and semi-arid landscape.
- Salt-soaked plain to the north of Kutch is the Great Rann.
- Its southern continuation, known as the Little Rann lies on the coast and southeast of Kutch.
- The Kathiawar Peninsula lies to the south of the Kutch.
- The Gir Range is located in the southern part of the Kathiawar peninsula.
- It is covered with dense forests and is famous as the home of the Gir lion.
- Mt. Girnar (1,117 m) is the highest point and is of volcanic origin.
Gujarat Plain
- The Gujarat Plain lies east of Kutch and Kathiawar and slopes towards the west and south-west.
- Formed by the rivers Narmada, Tapi, Mahi and Sabarmati
- The plain includes the southern part of Gujarat and the coastal areas of the Gulf of Khambat.
- The eastern part of this plain is fertile enough to support agriculture
Konkan Coast
- The Konkan coast is located in the south of the Gujarat plain.
- Konkan coast extends from Daman to Goa.
- It is a 720 km long coastline.
- This is the most submerged coastal plains of India.
- Konkan coast has some features of marine erosion including cliffs, shoals, reefs and islands in the Arabian Sea.
- The Thane creek around Mumbai is an important coastline of India which provides an excellent natural harbour.
Goan Coast
- Coast of Goa and Karnataka
- It is the narrowest coastal plain with an average width of 8-25 km, the maximum being 70 km near Mangalore.
- Sharavati river makes Gersoppa (Jog) Falls which is 271 m high.
Malabar Coast
- The Kerala Plain is also known as the Malabar Plain.
- Between Mangalore and Kanniyakumari.
- It is a wider and low-lying plain.
- The existence of lakes, lagoons, backwaters, spits, etc. is a significant characteristic of the Malabar coast.
- The backwaters, locally known as kayals are the shallow lagoons
- Largest among these is the Vembanad Lake
- Every year the famous Nehru Trophy Vallamkali (boat race) is held in Punnamada Kayal in Kerala.

Eastern Coastal Plains of India
- The Eastern coastline is extended from the Subarnarekha river along the West Bengal-Odisha border to Kanniyakumari.
- The Eastern coastal plain of India is broader and is an example of an emergent coast.
- There are well-developed deltas on the eastern coastline of India
- Deltas formed by the rivers flowing eastward into the Bay of Bengal, include Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri
- The Eastern coastline of India is emergent in nature and the continental shelf extends up to 500 km into the sea.
- It makes it difficult for the development of good ports and harbours.
- This plain is known as
- Northern Circars – Mahanadi to Krishna river
- Carnatic – Krishna to Cauvery river
Utkal Plain
- The Utkal Plain comprises coastal areas of Odisha.
- It includes the Mahanadi river delta.
- The most prominent physiographic feature of this plain is Chilika Lake.
- It is the biggest lake in the country and its area varies between 780 sq km in winter to 1,144 sq km in the monsoon months.
Andhra Plain
- South of the Utkal Plain and extends up to Pulicat Lake.
- Pulicat lake has been barred by a long sand spit known as Sriharikota Island
- The two deltas of Godavari and Krishna have merged with each other and formed a single physiographic unit.
- The combined delta has advanced by about 35 km toward the sea in recent years.
- Kolleru Lake which was once a lagoon at the shore but now lies far inland.
- This coastline of India lacks good harbours except for Vishakhapatnam and Machilipatnam.
Coromandel Coast
- Coromandel Coast of Tamil Nadu Plain stretches from Pulicat lake to Kanniyakumari.
- Pulicat Lake is the 2nd largest brackish water lagoon in India.
- The fertile soil and large-scale irrigation facilities have made the Cauvery delta (Thanjavur) the granary of South India.
- Coromandel Coast or Payan Ghat plain stretches from Krishna delta to Kanyakumari
Significance of the Coastal Plains in India
- Large parts of the coastal plains in India are covered by fertile soils on which different crops are grown.
- Coconut trees grow all along the coastline of India.
- The entire length of the coastline of India is dotted with big and small ports which help in carrying out trade.
- The sedimentary rocks of these plains are said to contain large deposits of mineral oil (KG Basin).
- Sands of Malabar coast have large quantities of Monazite sand, which can be used for nuclear power.
- Fishing is an important occupation of the people living in the coastal plains of India.
- Low-lying areas of Gujarat are famous for producing salt.
- Kerala’s backwaters are important tourist destinations.
- Goa provides good beaches. This is also an important tourist destination.
Some Important Beaches
- Marina, TN – The longest beach in India
- Kovalam, Kerala – Monazite and Limonite found here
- Girgaum Chowpatti, MH – Famous for Ganesh Chaturthi
- Alappuzha, Kerala – Venice of the East